Energy Force enables precise tax configuration and application to sales transactions. This document outlines the setup process for taxes and how they are applied.
Department Setup
Departments determine how items are taxed and are found at Main Menu / Supervisor Menu / Maintenance Menu / Maintenance Tables / Department.
Three key columns control taxation:
- Sales Tax — State Sales Tax.
- Fed Tax — Federal Excise Tax.
- Other — City tax, County tax, State Excise taxes, LUST tax, etc.

These columns are correlated back to Tax Types setup on Tax Groups. If a group is checked in the Department table, Energy Force applies the corresponding tax rates from the Tax Rate table, provided certain parameters are met.
Tax Group Setup
Tax Groups must be established before configuring tax rates at Main Menu / Supervisor Menu / Maintenance Menu / Maintenance Tables / Tax Group Setup.
- Standard groups include State Sales Tax, Federal Excise Tax, State Excise Tax, City Tax, and County Tax.
- Additional groups typically fall under Other.
- For each transaction, only one tax can be applied per group.
Key Fields:
- ID — Auto-generated, unmodifiable number.
- Description — Description of the Tax Group.
- Tax Type — Dropdown with options for Sales Tax, Federal Motor Fuel, or Other.

Use Code Setup
Use Codes manage special taxing situations, such as exemptions or adjusted rates based on usage (e.g., Agricultural, Residential, Commercial) and set up at Main Menu / Supervisor Menu / Maintenance Menu / Maintenance Tables / Use Code Maint.
- Use Codes are up to 3 alphanumeric characters with a description visible during tank setup.

Tax Rate Setup
Each tax rate is defined by a unique Tax ID, Tax Group, and Tax Description found at Main Menu / Supervisor Menu / Maintenance Menu / Maintenance Tables / Tax.
- Description — Appears on delivery tickets if itemized taxes are enabled in the order of Tax ID number.
- Do not delete taxes
- Taxes in Energy Force should never be deleted once they are set up. Doing so can lead to inconsistencies and affect historical data integrity.
- Tax rates can be modified to reflect the current rate. Historical transactions will retain the tax rates that were in effect at the time of the transaction.
- Inactivate and Create New Tax Rates
- If a change is required, inactivate the existing tax and create a new tax rate to reflect the updated information. This ensures that historical transactions remain accurate while enabling the system to reflect the current tax structure.
- When adding a new tax rate, ensure all relevant cross-reference tables in back-office software interfaces are updated to maintain data consistency.
- Geographical Information
- State — Required for state-specific taxes, including County, City, Township, and School District. Not required for Federal Taxes.
- County, Township, School District — Select the corresponding Master IDs from the maintenance tables by double-clicking the fields.
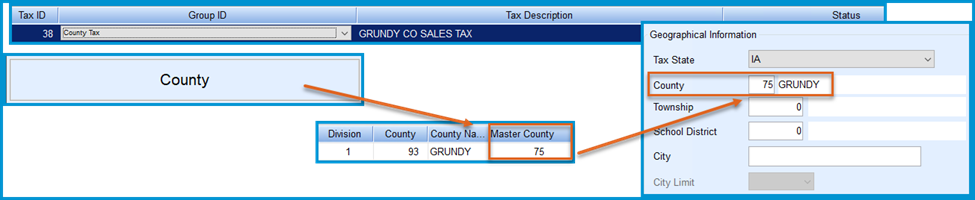
- State — Required for state-specific taxes, including County, City, Township, and School District. Not required for Federal Taxes.
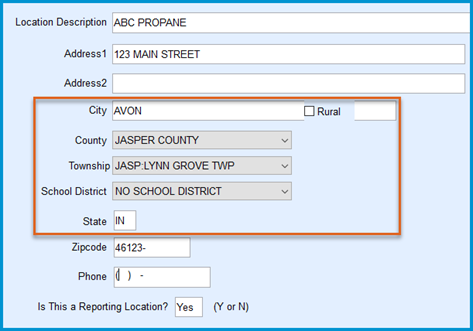
- City — Must match Tank Information exactly. City names should be entered with all CAPS.
- City Limit — For City Taxes, optionally set the tax to apply only to Urban or Rural tanks.
Example: If the tax is designated for Urban areas, tanks marked as Rural will not have the tax applied, as they are located outside the city limits. This allows for precise tax application based on geographic classifications. - Note on Federal Excise Taxes
- Non-Location-Based Taxation — Federal Excise Taxes are not tied to a delivery address or tank location. These taxes apply uniformly across all locations, ensuring a consistent rate regardless of where the tank or office is physically situated.
- Standard Rates — Examples of Federal Excise Tax rates include:
- Unleaded Gasoline: 18.4%
- Clear Diesel Fuel: 24.4%
- Miscellaneous Settings
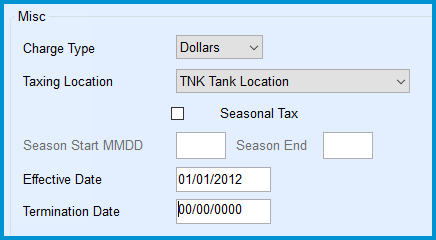
- Charge Type
- Dollars — Tax is a percentage of the sales amount.
- Gallons — Tax is a flat rate per gallon.
- Taxing Location
- TNK (Tank Location) — Based on tank's geographical attributes.
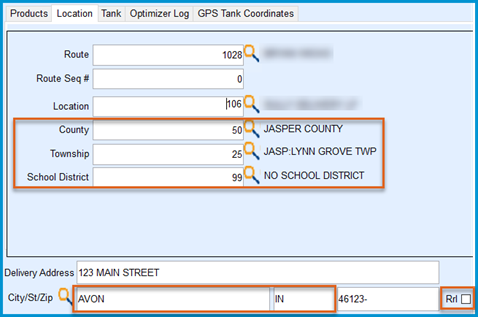
- POO (Point of Origin) — In this context, refers to the servicing location derived from the Master Tank Location attributes found at Main Menu / Supervisor Menu / Maintenance Menu / Maintenance Tables / Tank Location. This means that the POO is determined by identifying the specific servicing location assigned to a given tank or Energy Service site based on the data and parameters within the Master Tank Location attributes.
- TNK (Tank Location) — Based on tank's geographical attributes.
- Seasonal Tax — Configured to apply during specific date ranges. Enter Start and End Dates in MMDD format.
- Effective Dates
- Enter the Start date for the Tax Rate in MMDDYYYY format.
- The Termination Date can be left at 00/00/0000 for indefinite tax or an ending date can be entered.
Tax Rates
- Global or Specific Application
- To apply a tax to all products, use 0 for Division and Product in the Tax Rate table.
- For product-specific taxes, define Division and Product codes alongside the applicable Rates.
- For cooperative-based setups, all tax setups should be exclusively in Division 1.
- Use Codes — Different rates can be applied depending on usage.
Note: Avoid the 0 for all configuration when dealing with multiple states and point-of-origin taxation.

Compound Taxes
Compound Taxes, also known as tax on tax, are used in specific scenarios where a tax is applied to a subtotal that includes other taxes, rather than directly to the total sale amount. These taxes are calculated based on applicable components and factored into the overall total tax amount.
Key Features:
- Default Behavior — By default, taxes are calculated on the subtotal.
- Compound Tax Setup — In scenarios where a tax needs to be applied after other taxes have been calculated, Energy Force allows Tax Groups to be added to the Tax Setup. When a Tax Group is added, Energy Force calculates the included Tax Groups into a subtotal prior to applying that tax item. This setup ensures that a Compound Tax considers the total sale amount, including applicable taxes from defined Tax Groups, before applying itself.
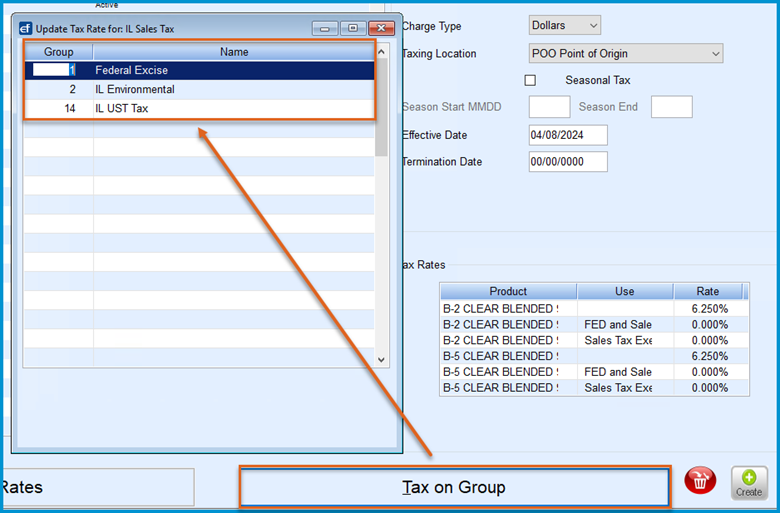
- Example Scenario — If a State Sales Tax needs to include the Federal Excise Tax in its taxable base, as seen in Illinois refined fuel taxation then,
- The Federal Excise Tax, Illinois Environmental Tax, and Illinois Underground Storage Tax are calculated and combined into a subtotal.
- The system applies the Illinois State Sales Tax to the subtotal, which includes the sale amount, Federal Excise Tax, Illinois Environmental Tax, and Illinois Underground Storage Tax.
- Configuration Steps —
- Navigate to the Tax on Group setup in the Tax Rate Maintenance table.
- Select the Tax ID for the compound tax you are configuring.
- Define the Tax Groups that need to be included in the base calculation before this tax is applied.
- Example Scenario — If a State Sales Tax needs to include the Federal Excise Tax in its taxable base, as seen in Illinois refined fuel taxation then,
Recommendations
- Documentation — Use clear, concise descriptions for Tax Groups and Tax Rates to avoid confusion.
- Testing — Verify all tax setups in a test environment before moving to production.
- Utilize the Test Sale feature in Energy Force on customer tanks to confirm correct tax application for various scenarios, including special use cases like Use Codes, Seasonal Taxes and Compound Taxes.
- Maintenance
- Regularly review tax rates for updates or expirations.
- Schedule periodic audits to verify compliance with local, state, and federal tax regulations.
- Maintain updated records of any changes to tax codes or business processes to ensure alignment with tax setups.




